About event gateways
ColdFusion event gateways are ColdFusion elements that let ColdFusion react to or generate external events or messages in an asynchronous manner. Event gateways let a ColdFusion application handle information that does not come through an HTTP request. For example, you can use event gateways to handle instant messages, short messages from mobile devices, or messages sent to a TCP/IP port.
The event gateway mechanism has the following major features:
- ColdFusion event gateways do not require HTTP requests. ColdFusion developers can write ColdFusion gateway applications without using any CFM pages (just CFCs).
- ColdFusion CFCs can use event gateways to listen for and respond directly to external events.
- Event gateways operate asynchronously. A gateway typically gets a message and dispatches it for processing, without requiring or waiting for a response.
- ColdFusion developers can create event gateways to handle any kind of event that a Java application can receive.
ColdFusion includes several product-level event gateways, such as a gateway for the XMPP (Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol) instant messaging protocol. Adobe also provides the source for several example gateways, such as a generalized socket gateway, that you can extend to handle your specific needs. You can also write your own gateways in Java to handle other event or messaging technologies supported by the Java runtime or by third-party providers, such as gateways for additional instant messaging protocols, gateways for specific ERP systems, or other protocols, such as NNTP.
Using event gateways
Because event gateways provide a generalized asynchronous messaging mechanism, you can use them with many kinds of event or messaging resources. For example, ColdFusion includes gateways (either product quality, or lighter weight example gateways) for communicating between ColdFusion applications and the following types of resources:
- Mobile phones and other devices that support short messaging services (SMS)
- XMPP or IBM Sametime Instant message clients
- Java Sockets (which let your ColdFusion application communicate with TCP/IP-based devices and programs, such as Telnet terminal clients).
- Java Messaging Service (JMS) resources, such as storefront sales order handling systems.
Event gateways are not limited to sending or receiving information using communications protocols. For example, ColdFusion includes an example event gateway that monitors changes to a directory and invokes a CFC method whenever the directory changes. ColdFusion also includes an event gateway that lets a CFML application "call" a CFC asynchronously and continue processing without getting a response from the CFC.
Just as you can create event gateways that serve many different event or messaging based technologies, you can write many kinds of applications that use them. Just a few examples of possible gateway uses include the following.
Server to client push examples
- An application that sends an instant message (IM) or SMS text message to a person who can approve a purchase order, get a response, and mark the purchase order as approved or denied.
- A bot that notifies users through their preferred messaging method (cell phone, instant messaging, or even e-mail) when watch list stock goes up, and offers to buy or sell the stock immediately.
- An application that authenticates web users by sending them an SMS message that includes code that they must to enter into the browser in order to proceed.
- A menu-based SMS application that lets users get information from any of several web service data providers. ColdFusion includes a SMS menuing example int the gateways/cfc directory.
- A instant messaging application that takes messages from users to technical support and assigns and directs the messages to the most available support staff member. The application could also log the user ID and session, and you could use ColdFusion to generate usage reports.
- A directory lookup robot IM "buddy" that responds to messages chat contain an employee's name with the employee's phone number or buddy ID.
- A JMS subsystem that publishes status updates that are consumed by business intelligence systems.
- A system that monitors and publishes download events from a website.
Event gateway terms and concepts
This document uses the following terms when referring to event gateways:
Event: A trigger that ColdFusion can receive from an external source. ColdFusion event gateways receive events.
Message: The information provided by an event. In ColdFusion, a message is the data structure that the event gateway receives when an event is triggered.
Event gateway: Java code that receives events and sends them to and from ColdFusion application code. This document uses the term event gateway, without the word type or instance, to refer to the general concept of a ColdFusion event gateway. Where the context makes the meaning obvious, the term can also refer to event gateway type or event gateway instance.
Event gateway type: A specific event gateway implementation, represented by a Java class. Each event gateway type handles messages belonging to a particular a communications method or protocol, such as short message service (SMS), an instant messaging protocol, or Sockets. You generally have one event gateway type per communication protocol. You configure each event gateway type on the Gateway Types page in the Event Gateways area in the ColdFusion Administrator.
Event gateway instance: A specific instance of an event gateway type class. You configure each event gateway instance on the ColdFusion Gateways page by specifying the event gateway type, an ID, the path to the event gateway application CFC that uses this instance, and a configuration file (if needed for the selected event gateway type). You can have multiple event gateway instances per event gateway type, for example, for different event gateway applications.
Event gateway application: One or more CFCs and any supporting CFM pages that handle events from an event gateway instance and send messages using the event gateway instance. The event gateway application is not part of an event gateway instance, but the code that is responsible for processing event messages to and from the instance.
Event gateway listener: Code in an event gateway that receives events from an event source and passes them to the ColdFusion gateway service for delivery to a CFML listener CFC.
Listener CFC: A CFC that contains one or more methods that respond to incoming messages from one or more event gateway instances. Part of an event gateway application.
ColdFusion gateway service: The part of ColdFusion that provides underlying support for event gateways, including a path between an event gateway instance and listener CFCs.
How event gateway applications work
The following diagram shows the architecture of ColdFusion event gateway applications:
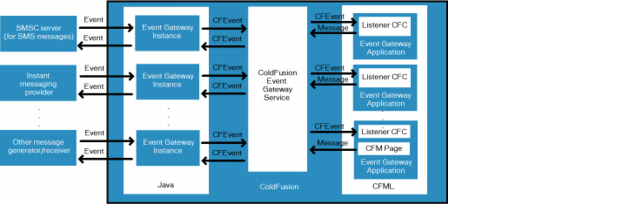
Typically, a ColdFusion event gateway instance, a Java object, listens for events coming from an external provider. For example, a general socket event gateway listens for messages on an IP socket, and an SMS event gateway receives messages from an SMSC server.
Each event gateway instance communicates with one or more listener CFCs through the ColdFusion event gateway service. The listener CFCs receive CFEvent object instances that contain the messages, process them, and can send responses back to the event gateway, which can send the messages to the external resources.
Alternatively, a ColdFusion application can initiate a message by calling a ColdFusion function that sends the message to the event gateway. The event gateway then forwards the message to an external resource, such as an instant messaging server. A CFC in the application listens for any responses to the sent message.
Some event gateways can be one-way: they listen for a specific event and send it to a CFC, or they get messages from a ColdFusion function and dispatch it, but they do not do both. The example DirectoryWatcherGateway listens for events only, and the asynchronous CFML event gateway receives messages from CFML only. (You could even say that the directory watcher gateway doesn't listen for events; it creates its own events internally by periodically checking the directory state.) For information on the asynchronous CFML event gateway, see Using the CFML event gateway for asynchronous CFCs.
Java programmers develop ColdFusion event gateways by writing Java classes that implement the coldfusion.eventgateway.Gateway interface. ColdFusion event gateways normally consist of one or more threads that listen for events from an event provider, such as a Socket, an SMSC server, or some other source. The event gateway sends event messages to the ColdFusion event gateway service message queue, and provides a method that gets called when an event gateway application CFC or CFM page sends an outgoing message.
The event gateway class can also do the following:
- Provide the ColdFusion application with access to a helper class that provides event gateway-specific services, such as buddy-list management or connection management.
- Use a file that specifies configuration information, such as IP addresses and ports, passwords, and other ID information, internal time-out values, and so on.
About developing event gateway applications
ColdFusion application developers write applications that use event gateways. The person or company that provides the event gateway supplies gateway-specific information to the ColdFusion developer. This information must include the structure and contents of the messages that the ColdFusion application receives and sends to the event gateway, plus any information about configuration files or helper methods that the ColdFusion application might use.
The ColdFusion developer writes a CFC that listens for messages. Many event gateway types send messages to a listener CFC method named onIncomingMessage. A minimal event gateway application might implement only this single method. More complex event gateway types can require multiple CFC listener methods. For example, the ColdFusion XMPP IM event gateway sends user messages to the onIncomingMessage CFC method, but sends requests to add buddies to the onAddBuddyRequest CFC method.
Depending on the event gateway and application types, the event gateway application might include CFM pages or CFC methods to initiate outgoing messages. The application also might use an event gateway-specific GatewayHelper object to do tasks such as getting buddy lists in IM applications or getting a messaging server's status.
The ColdFusion application developer also configures an event gateway instance in the ColdFusion Administrator, and possibly in a configuration file. The ColdFusion Administrator configuration information specifies the listener CFC that handles the messages from the event gateway and other standard event gateway configuration details. The configuration file, if required, contains event gateway type-specific configuration information.

