XML document structures
An XML document object is a structure that contains a set of nested XML element structures. The following image shows a section of the cfdump tag output for the document object for the XML in A simple XML document. This image shows the long version of the dump, which provides complete details about the document object. Initially, ColdFusion displays a short version, with basic information. Click the dump header to change between short, long, and collapsed versions of the dump.
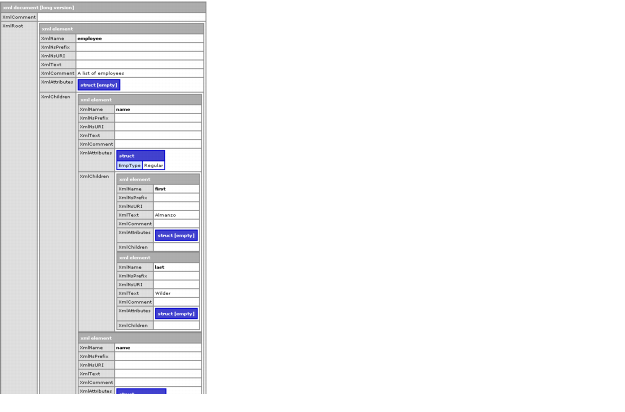
The following code displays this output. It assumes that you save the code in a file under your web root, such as C:\Inetpub\wwwroot\testdocs\employeesimple.xml
<cffile action="read" file="C:\Inetpub\wwwroot\testdocs\employeesimple.xml"
variable="xmldoc">
<cfset mydoc = XmlParse(xmldoc)>
<cfdump var="#mydoc#">
At the top level, the XML document object has the following three entries:
|
Entry name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
XmlRoot |
Element |
The root element of the document. |
|
XmlComment |
String |
A string made of the concatenation of all comments on the document, that is, comments in the document prologue and epilog. This string does not include comments inside document elements. |
|
XmlDocType |
XmlNode |
The DocType attribute of the document. This entry only exists if the document specifies a DocType. This value is read-only; you cannot set it after the document object has been created This entry does not appear when the cfdump tag displays an XML element structure. |
Each XML element has the following entries:
|
Entry name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
XmlName |
String |
The name of the element; includes the namesapce prefix. |
|
XmlNsPrefix |
String |
The prefix of the namespace. |
|
XmlNsURI |
String |
The URI of the namespace. |
|
XmlText or XmlCdata |
String |
A string made of the concatenation of all text and CData text in the element, but not inside any child elements. When you assign a value to the XmlCdata element, ColdFusion puts the text inside a CDATA information item. When you retrieve information from document object, these element names return identical values. |
|
XmlComment |
String |
A string made of the concatenation of all comments inside the XML element, but not inside any child elements. |
|
XmlAttributes |
Structure |
All of this element's attributes, as name-value pairs. |
|
XmlChildren |
Array |
All this element's children elements. |
|
XmlParent |
XmlNode |
The parent DOM node of this element. This entry does not appear when the cfdump tag displays an XML element structure. |
|
XmlNodes |
Array |
An array of all the XmlNode DOM nodes contained in this element. This entry does not appear the cfdump tag when displays an XML element structure. |
The following table lists the contents of an XML DOM node structure:
|
Entry name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
XmlName |
String |
The node name. For nodes such as Element or Attribute, the node name is the element or attribute name. |
|
XmlType |
String |
The node XML DOM type, such as Element or Text. |
|
XmlValue |
String |
The node value. This entry is used only for Attribute, CDATA, Comment, and Text type nodes. |
The following table lists the contents of the XmlName and XmlValue fields for each node type that is valid in the XmlType entry. The node types correspond to the objects types in the XML DOM hierarchy.
|
Node type |
XmlName |
xmlValue |
|---|---|---|
| CDATA | #cdata-section |
Content of the CDATA section |
| COMMENT | #comment |
Content of the comment |
| ELEMENT |
Tag name |
Empty string |
| ENTITYREF |
Name of entity referenced |
Empty string |
| PI (processing instruction) |
Target entire content excluding the target |
Empty string |
| TEXT | #text |
Content of the text node |
| ENTITY |
Entity name |
Empty string |
| NOTATION |
Notation name |
Empty string |
| DOCUMENT | #document |
Empty string |
| FRAGMENT | #document-fragment |
Empty string |
| DOCTYPE |
Document type name |
Empty string |
The XML document object and all its elements are exposed as DOM node structures. For example, you can use the following variable names to reference nodes in the DOM tree that you created from the XML example in A simple XML document:
mydoc.XmlName mydoc.XmlValue mydoc.XmlRoot.XmlName mydoc.employee.XmlType mydoc.employee.XmlNodes[1].XmlType

